We’re committed to making digital content accessible to as many people as possible at Liverpool John Moores University. This article is one in a series of accessibility tips to help you improve the digital environment for everyone. We would like you to adopt these tips as part of your practice.
There are some simple steps you can take in Word documents or web pages like those in Canvas to make your content accessible.
People with visual impairments sometimes use screen reader software to read your document or webpage out loud. Screen readers have no way of understanding an image without you telling it what it contains. This is where the Alternative Text or Alt Text field can help. Screen readers read out text in the ‘Alt Text’ field allowing users to understand the purpose of the image. If the image contains important information for the reader you need to ensure that you include this information in the Alt Text field. You can create Alt Text for shapes, pictures, charts, SmartArt graphics, or other objects.
How to Apply Alt Text
Depending on whether you’re using Word or adding content to a web page like those in Canvas, the process may be slightly different.
Word
Once your image has been added, open the ‘Picture Format’ tab and then click on the ‘Alt Text’ option.
The same principle applies in Canvas, simply select your text and use the ‘paragraph’ box to select an appropriate heading:
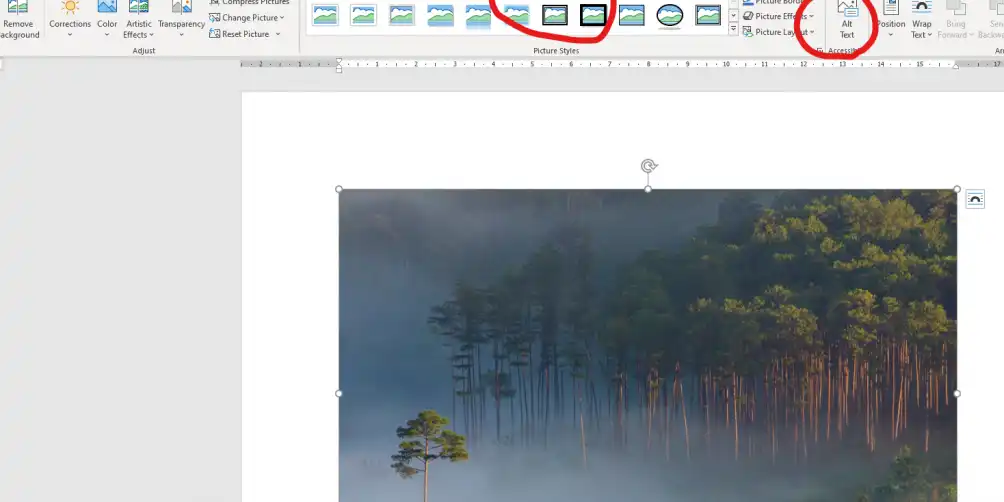
The Alt Text Panel in word, contains a section where you can add Alternative Text, there’s also a ‘Generate Description for me’ button, but you will need to ensure that the information that you want to convey is accurate. Graphs and Charts can also be summarised here.
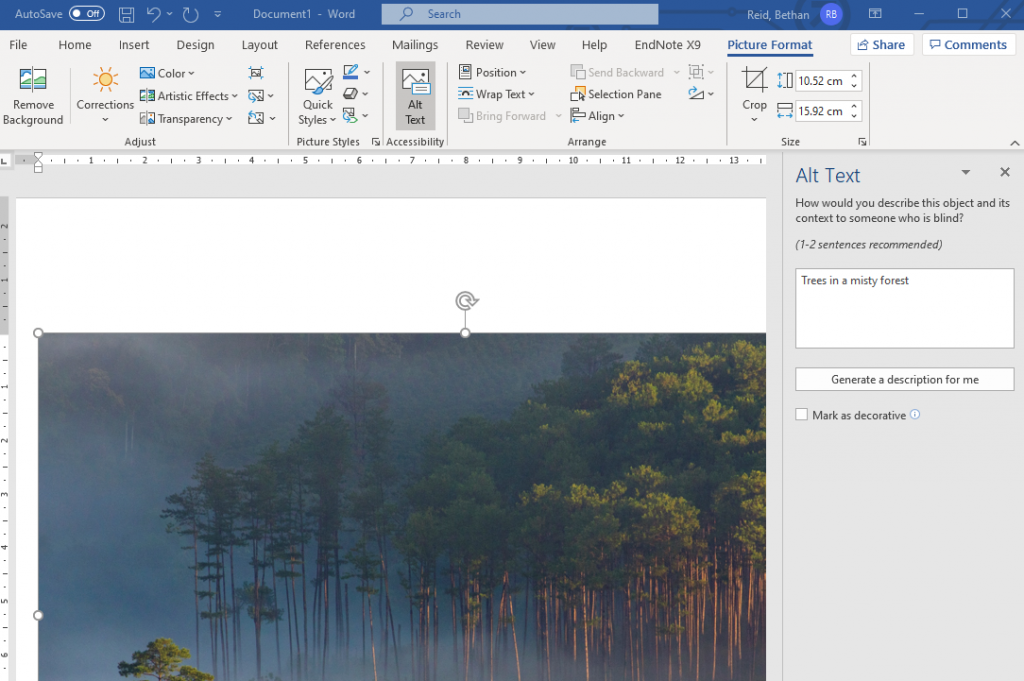
Excluding Alt text or marking your image as decorative, ensures that the image is ignored by assistive technologies.
Microsoft Guide: Add alternative text to a shape, picture, chart, SmartArt graphic, or other object
Canvas
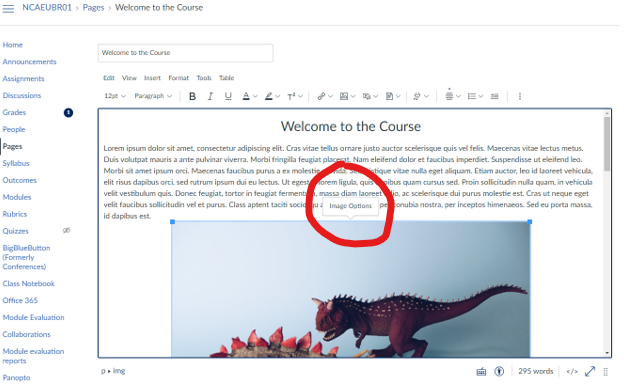
You can also add Alt Text to your images in Canvas. Simply click on your image to view the ‘Image Options’ button.
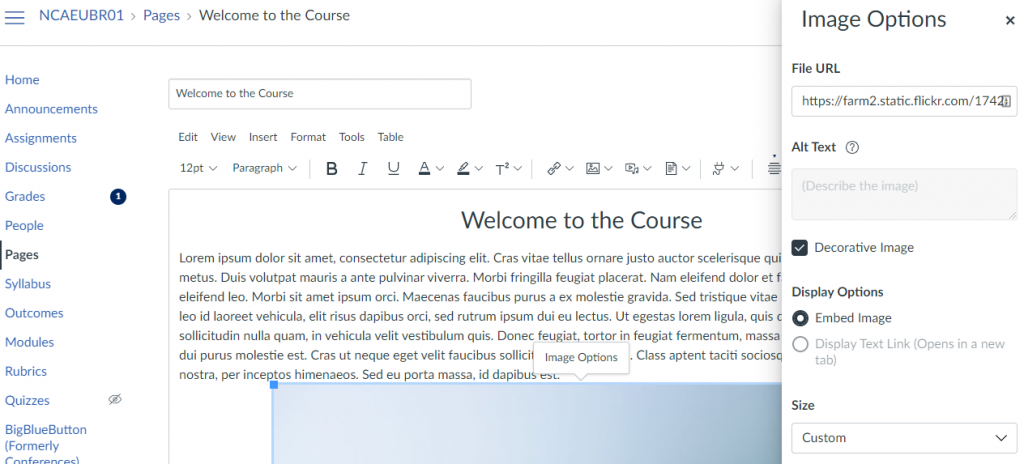
Similarly to MS Word, in Canvas a panel appears where you can add descriptive information about your image; or mark it as decorative to ensure that the image is ignored by assistive technologies.
For more information on how to use Alt Text, please see the Microsoft article Everything you need to know to write effective alt text.
Effective Alt Text
Now that you know how to add Alt Text, it’s equally important to understand how to write effective Alt Text. You should convey the purpose of the image in a sentence or two. Dont repeat the surrounding textual content in the Alt Text or include “an image of”. Diagrams and charts will require more detailed information, again conveying the purpose of diagram or chart.
Image Example
- A bad example of Alt Text for this image would be: Image of a dog.
- A good example of Alt Text for this image would be: My dog paddy half asleep.
Chart Example
- A bad example of a chart would be: A bar chart showing sales over time.
- A good example of a chart would include: A bar chart showing sales over time. In July, sales for brand A surpassed sales for brand B and kept increasing throughout the year.
When not to apply Alt Text
Not all images require Alt text, if you’re using an image purely for decorative purposes, and it does not convey information, then you can mark it as a ‘decorative image’. This ensures that screen readers skip this item of content and will continue to the next items of content. You do not need to add any alternative text for these images.
Further Resources
- What is alternative text? How do I write it for images, charts, and graphs?Links to an external site.
- Everything you need to know to write effective alt text.Links to an external site.
Accessibility in Digital Education Design Project (AiDED)
The Teaching and Learning Academy’s AiDED vision is to use the digital learning environment to help all our students improve their life chances. Find out more about accessibility and the AiDED project over on our AiDED Project page.

